Introduction
Dr. Sławomir Pastor, who established Stomatologia Pastor in Legnica, Poland, has been able to achieve remarkable outcomes in his implant-prostheses restorations with precision, speed, and effectiveness. In one of his latest cases, Dr. Pastor has provided excellent results using an immediate loading protocol with the PIC system.
Clinical case
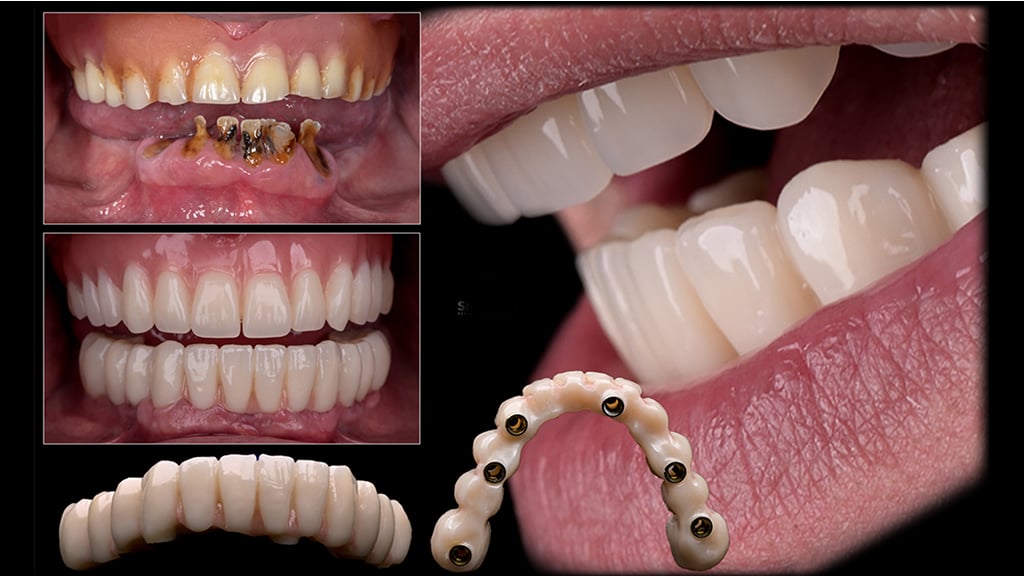
 A 48-year-old patient came to Dr. Pastor’s office to replace missing teeth in his mandible. An implant-prosthetic treatment in the mandible with an All-On-6 procedure with immediate implantation and immediate loading was proposed by Dr. Pastor and his team.
A 48-year-old patient came to Dr. Pastor’s office to replace missing teeth in his mandible. An implant-prosthetic treatment in the mandible with an All-On-6 procedure with immediate implantation and immediate loading was proposed by Dr. Pastor and his team.
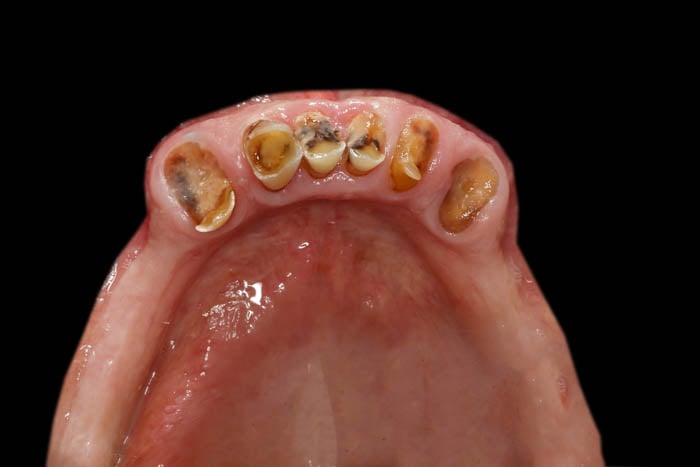 Residual dentition in the mandible.
Residual dentition in the mandible.
Intraoral scanning and radiological studies (OPG & CBCT) were performed, as well as photographic documentation. The files were sent to the prosthodontic laboratory for planning and preparation of surgical templates.
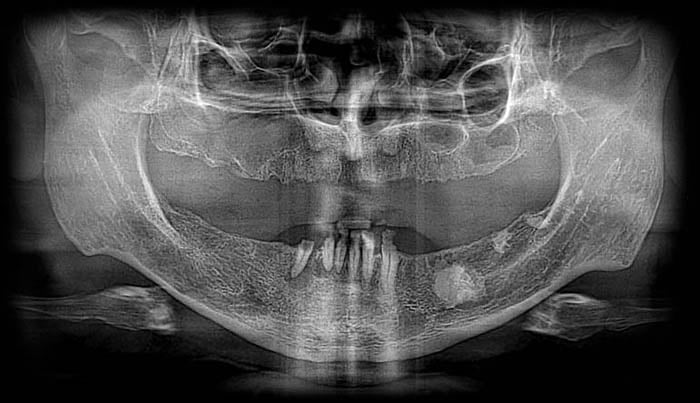 The OPG radiograph showed edentulousness in the maxillary range, and numerous periapical lesions in the roots of canines and incisors in the mandible. It also showed changes in the thickness of the spongiosa bone tissue in the mandibular body on the left side.
The OPG radiograph showed edentulousness in the maxillary range, and numerous periapical lesions in the roots of canines and incisors in the mandible. It also showed changes in the thickness of the spongiosa bone tissue in the mandibular body on the left side.
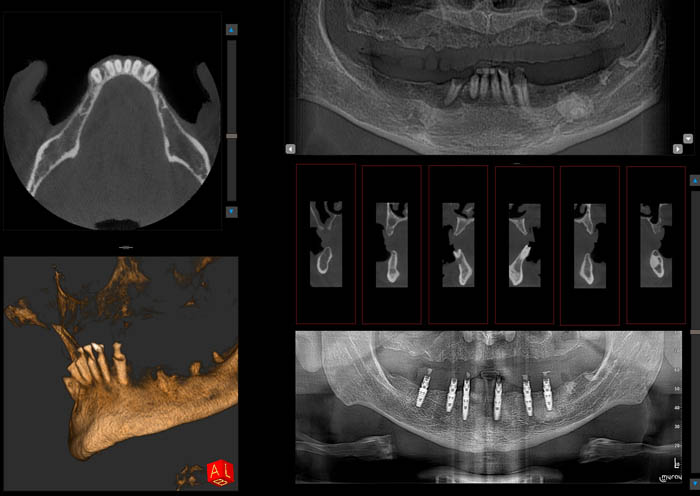
The radiographic files and images were combined in the exocad® software and planning of the future prosthetic work began. The exocad® platform offers the advantage of enabling comprehensive treatment planning.
The implant position planning was done with the exoplan software to design the surgical templates. Using exoplan, the next step is the design of the mucosa-supported surgical template. Designing the surgical template in exoplan allows the technician to create the template according to desired preferences.
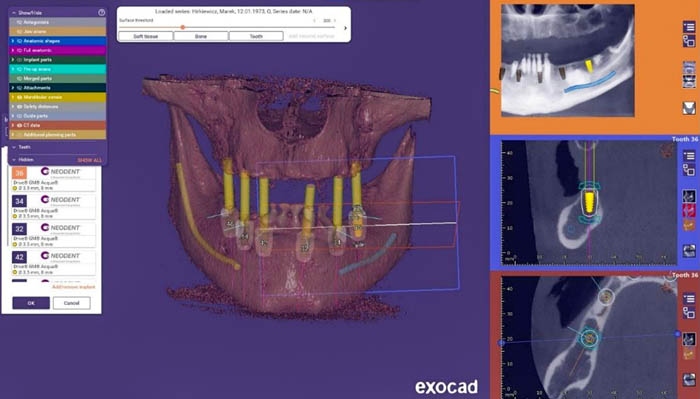
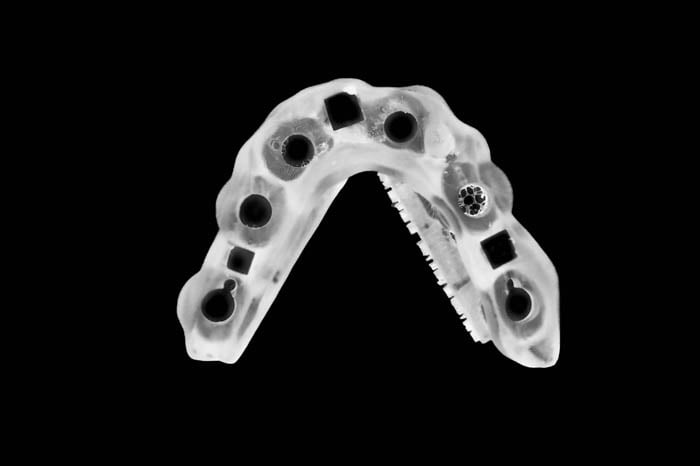
The visible mucosal-supported surgical template is created using the pilot drill from the DIO system to mark implant placement. The further osteotomy performed for this patient is done free-hand. After reviewing the treatment plan, the patient signed a written consent form to allow the doctor to perform the procedure under local anesthesia.
 Pre-medication:
Pre-medication:
- 2.0 Amoxicillin taken orally 1 hour before surgery
- 1000g of paracetamol taken orally
- Dexak 50 mg taken orally
- Anesthesia Dentocaine taken nasally
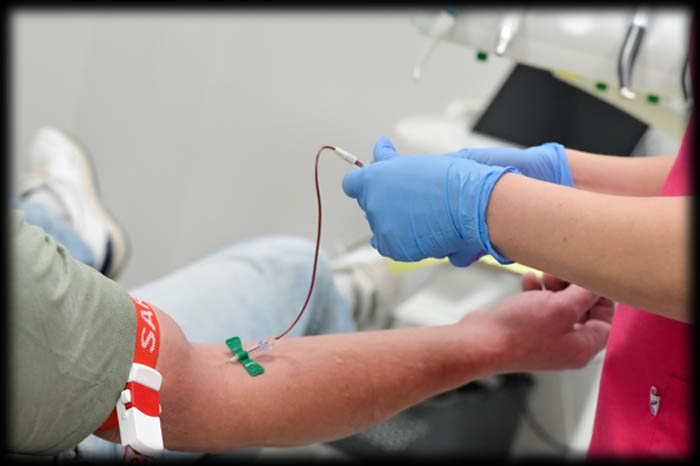
- Blood drawn to obtain A-PRF
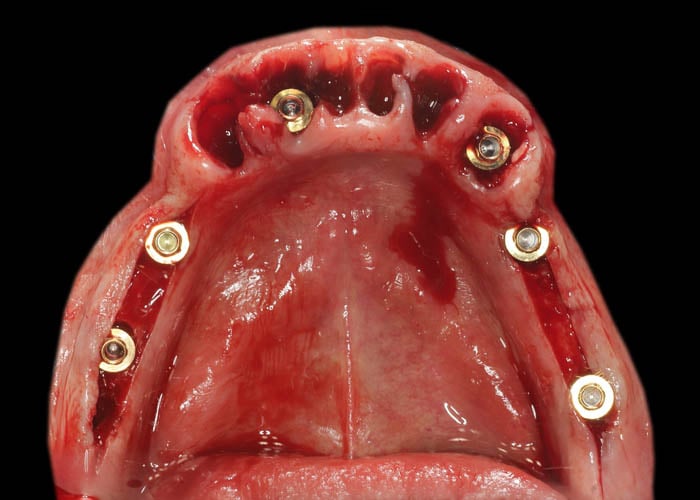 After the implants were inserted, the appropriate multi unit abutments were selected. There is a visible open site at implant position 36. This results in a lack of primary stabilization due to the extremely poor quality of the bone.
After the implants were inserted, the appropriate multi unit abutments were selected. There is a visible open site at implant position 36. This results in a lack of primary stabilization due to the extremely poor quality of the bone.
Due to the visible open site at implant position 36, the treatment plan was modified, and an implant was placed at position 35, done free-hand.
 An osteotomy took place in implant position 36. The alveoli and spaces that remained after the removed periodontal lesions were provided with allogenic cortical spongy bone from a tissue bank. The sockets and the exposed body of the mandible were treated with A-PRF and the edges of the wounds were sutured.
An osteotomy took place in implant position 36. The alveoli and spaces that remained after the removed periodontal lesions were provided with allogenic cortical spongy bone from a tissue bank. The sockets and the exposed body of the mandible were treated with A-PRF and the edges of the wounds were sutured.
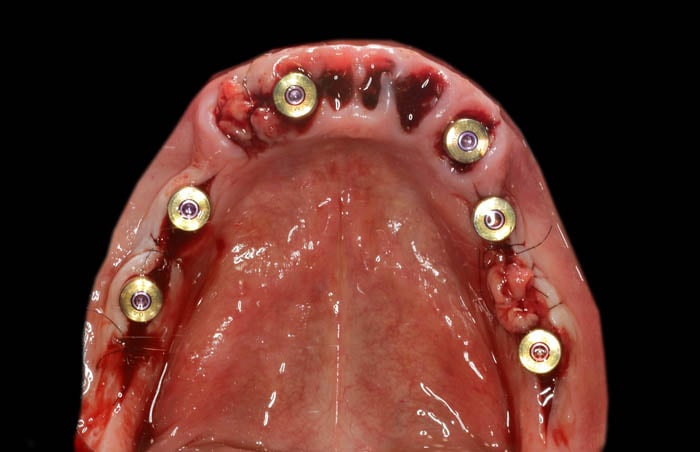 Post-procedure view of the mandible with healing screws in place on-top of multi-unit DAS abutments.
Post-procedure view of the mandible with healing screws in place on-top of multi-unit DAS abutments.
After the implant procedure, a biostimulation laser was used as a standard procedure for irradiation. Additionally, an OPG radiological scan was performed. This is aimed at creating space for the formation of a safe biological zone and obtaining long-term stable gingival and bone conditions. This OPG is also taken with the aim of creating a space for long-term stable gingival and bone conditions.
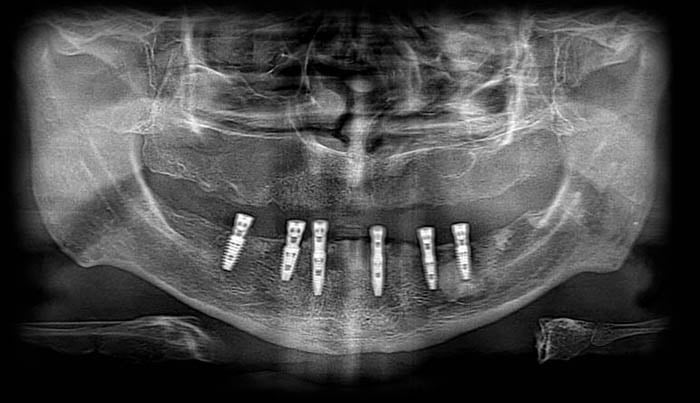
Control OPG showing lower jaw with placed implants and multi-units.
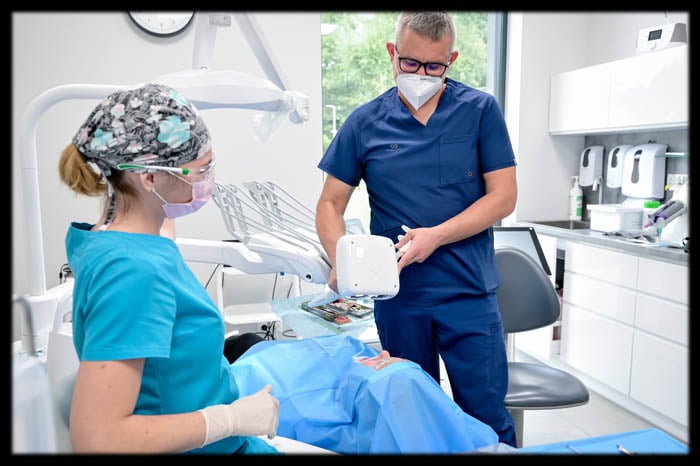
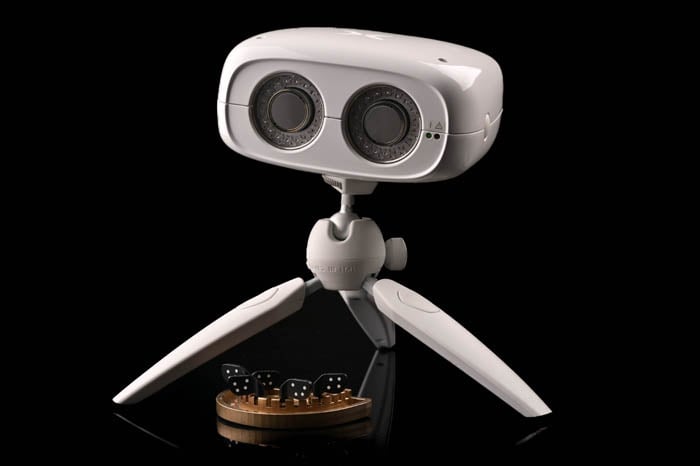 The PIC system was used to capture the positions of the implants. The PIC system is a fast and precise tool for measuring implant positions using photogrammetry technology.
The PIC system was used to capture the positions of the implants. The PIC system is a fast and precise tool for measuring implant positions using photogrammetry technology.
The PIC system records implant positions quickly, achieving precise measurements even with uncontrollable factors such as patient head movements. The implant positions measured using PIC transfers, which are 3D-coded photogrammetry abutments screwed to the patient's implants that provide the reference for measuring the absolute interrelated vector positions of the implants in the mouth based on more than 1,000 reference points.
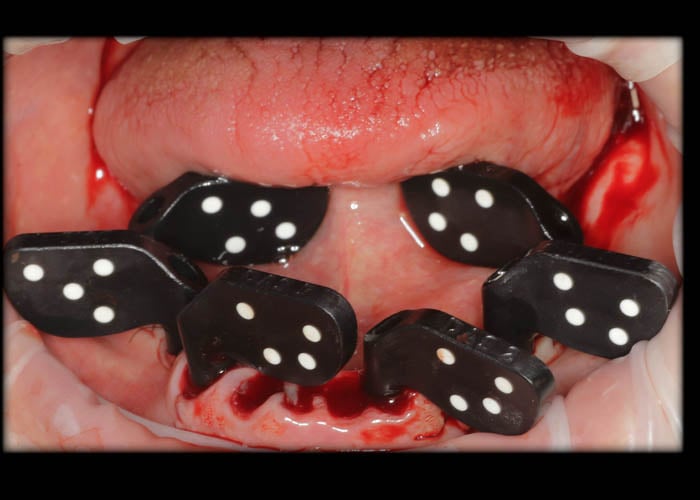
The PIC system capture takes place in under a minute, and can be performed direct to implant on the bone or tissue level, as well as at the abutment level with transepithelial abutments.
The PIC system generates a PIC file that contains only the interrelated implant positions and angulations. This PIC file is exported in the open STL format that can be used directly in exocad®.
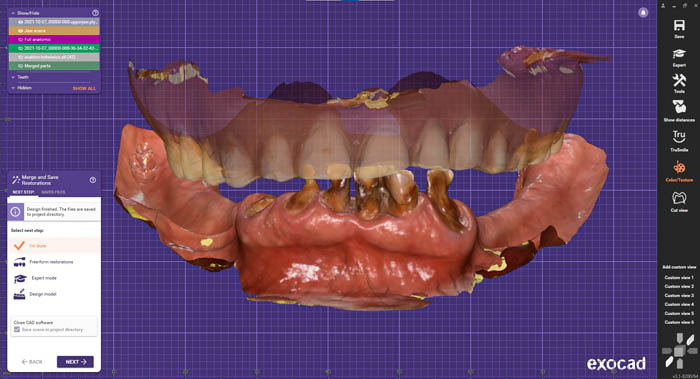
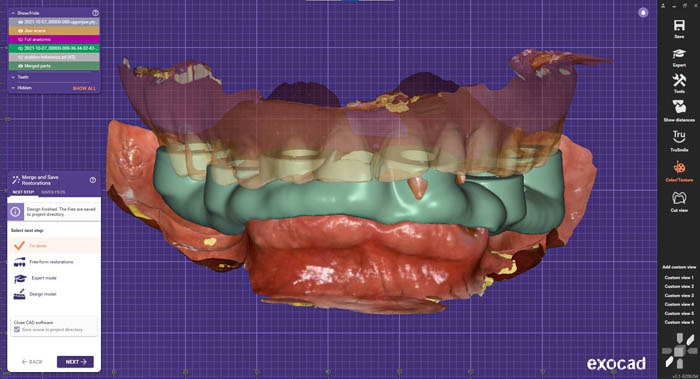
The second component is intraoral scanning of the soft tissues, which is imported into exocad®, along with the PIC file, in order to complete the digital model of the patient.
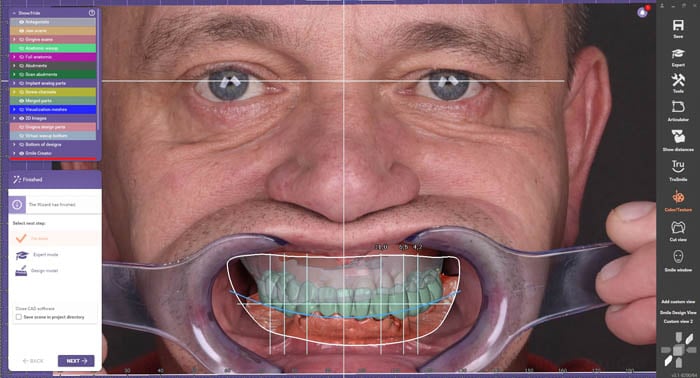
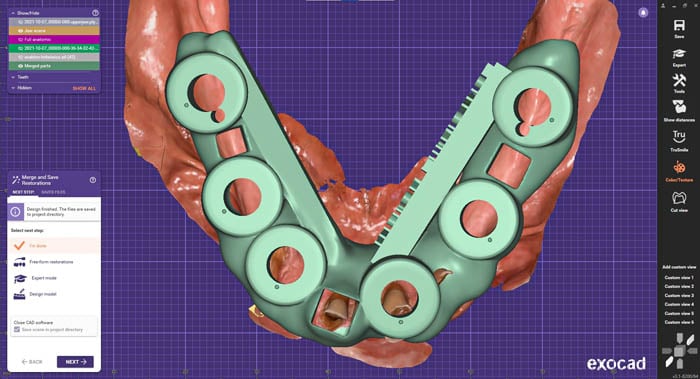
The design stage of the temporary bridge after immediate implant surgery is continued in exocad®. This design included the use of titanium bases made for multi-units.
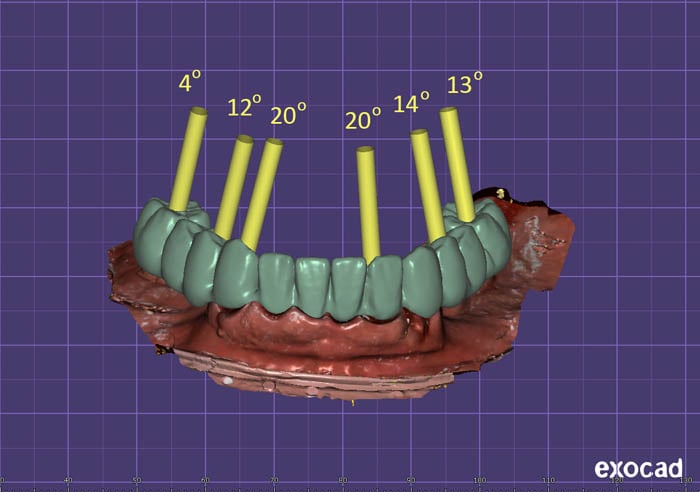 Bridge design.
Bridge design.
A 12-point bridge supported by 6 implants was screwed in 5 hours after the scan. At the same time, an individual tray was designed and printed from the intraoral scans along with occlusal shafts with the planned occlusal height. The proposed treatment called for the fabrication of a new complete denture to rebuild a proper occlusal plane. The provisional was placed and new records were taken, taking into account the new vertical dimension after the change of the upper jaw.
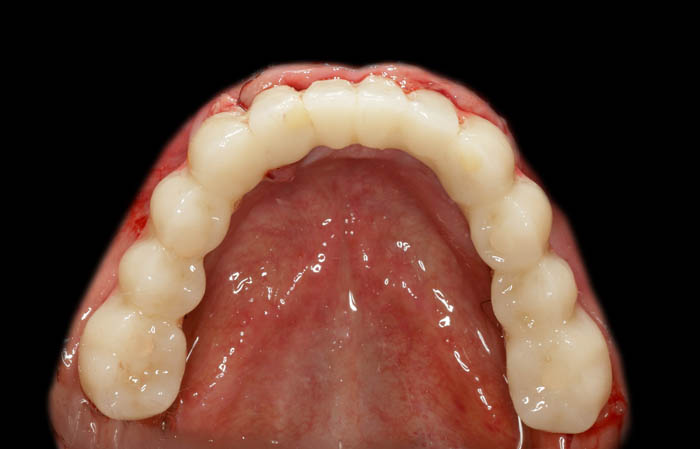
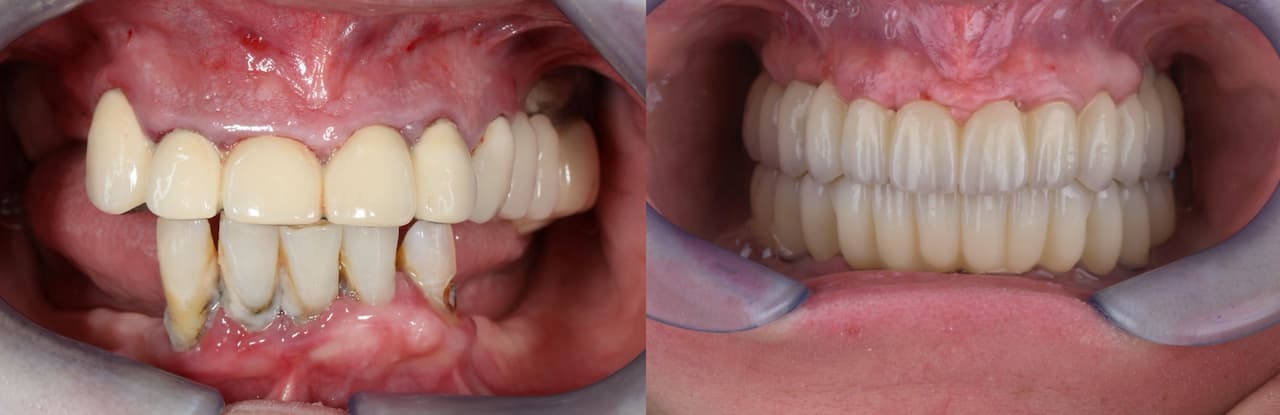
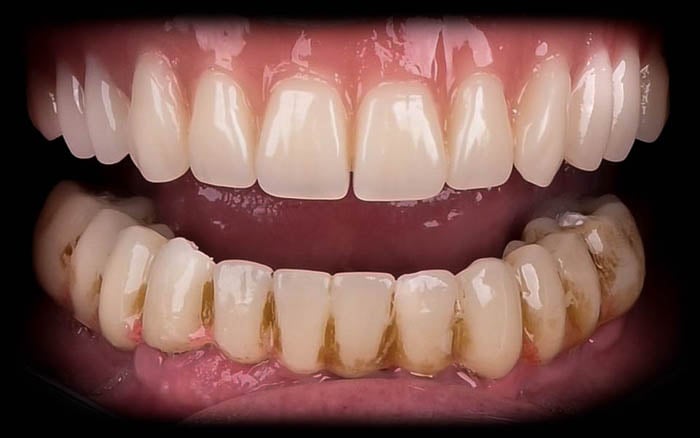 3 months after from the procedure, the final prosthetic restoration was planned. There are visible nicotine deposits on temporary restoration (PMMA milled bridge painted with Optiglaze GC). The soft tissue condition is satisfactory. The patient has no concerns or comments.
3 months after from the procedure, the final prosthetic restoration was planned. There are visible nicotine deposits on temporary restoration (PMMA milled bridge painted with Optiglaze GC). The soft tissue condition is satisfactory. The patient has no concerns or comments.
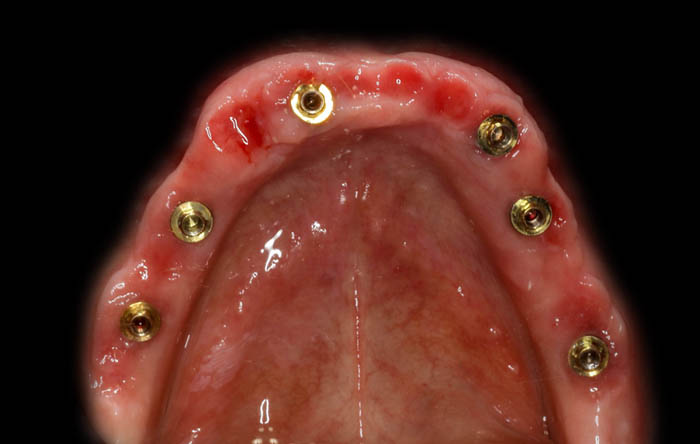
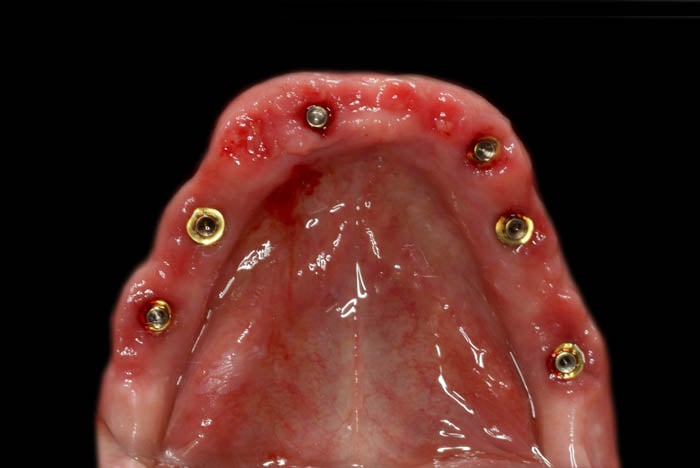
This was the condition after unscrewing the temporary bridge. The keratinized gingival zone has significantly widened and there is visible shaping of the gingival garland. The gingiva has stabilized, and to attain the appropriate emergence profile, a revision of the mucosal margin was performed, which was adjusted to match the current state of the gingiva.
A repeated intraoral scan included:
- A scan of the upper arch with a complete prosthesis
- A scan of the lower arch with a temporary PMMA bridge
- Registration of the occlusion
- A scan of the gingival mask after the PMMA bridge was unscrewed and the multi-units were moved to the lower jaw
Again, PIC transfers were screwed on, and the PIC system measured the implant positions, allowing for a passive fit for the final prosthesis. Achieving passivity with the final prosthetic is accomplished by using the PIC system to record the implant positions. This method eliminates the need for titanium bases to reinforce the monolithic zirconium oxide prosthesis.
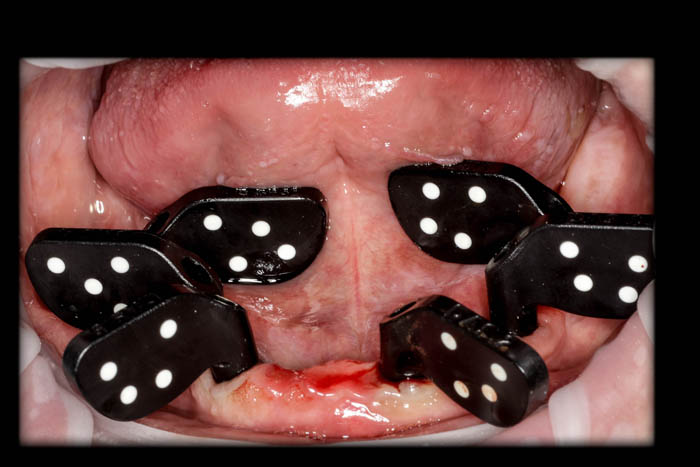
Prior to implementing the PIC system, the full-zirconia crown was susceptible to fracture because of inadequate passivity and the stresses generated after the prosthesis was screwed into position.
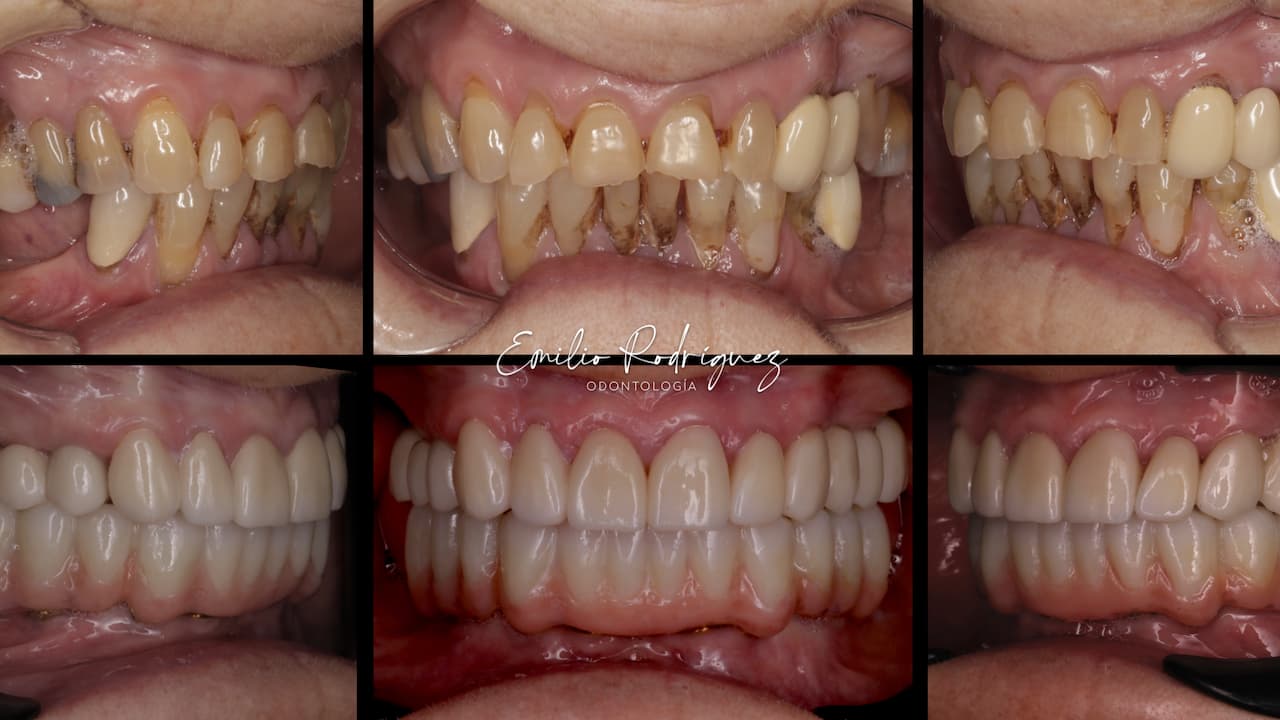
A close-up of the final restoration, consisting of a monolithic structure that is milled from zirconia and glued titanium bases, which can be redirected using the Dynamic Abutment Solutions system. The mucosal part is constructed from polished zirconia, which is currently the preferred material for interacting with soft tissues.
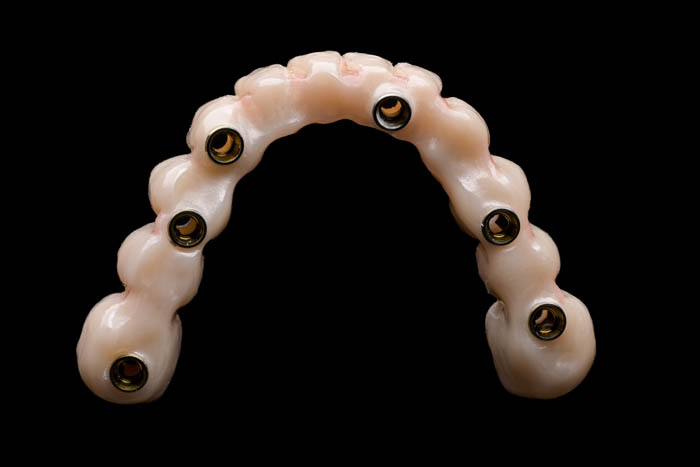
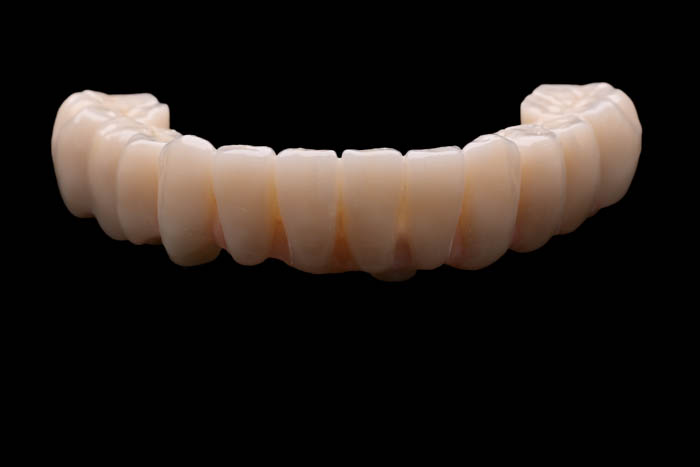
Thanks to the use of digital protocols, such as the PIC system, as well as milling and printing CAD/CAM technology, we are now enabled to provide patients with temporary restorations in a single day, starting with planning and concluding with prosthetic procedures.

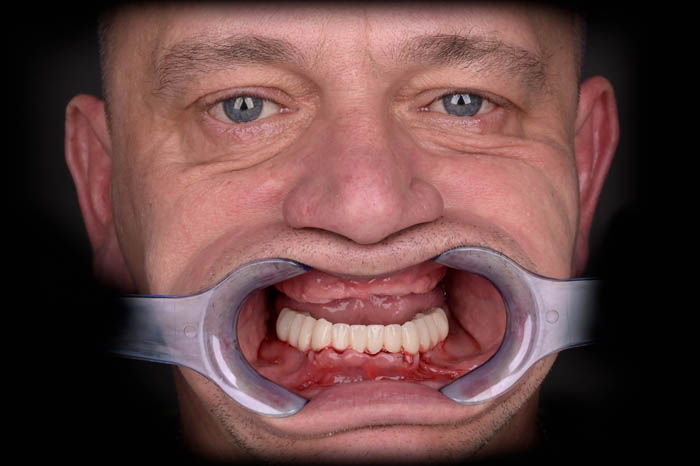
A view of a satisfied patient!
The entire procedure took 12 hours, from start to finish. The next stage of treatment will be an All-On-6 implant prosthetic treatment in the upper jaw.
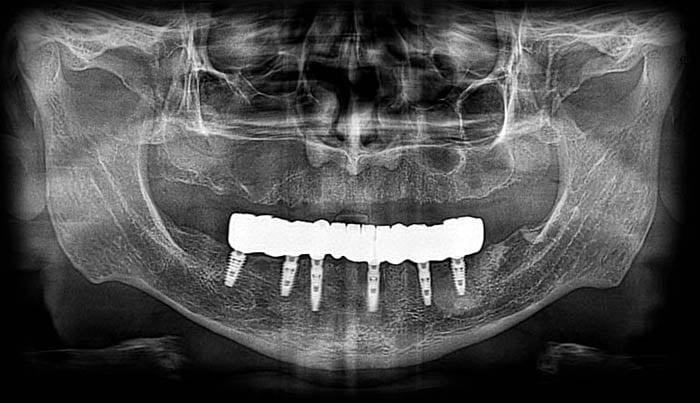
Control OPG scan performed after 12 months
Upon examination of the patient's mouth, there were no clinical indications of inflammation at the implants, and the patient reported no complaints. However, a follow-up panoramic radiograph revealed slight demineralization of the bone surrounding implant 46.
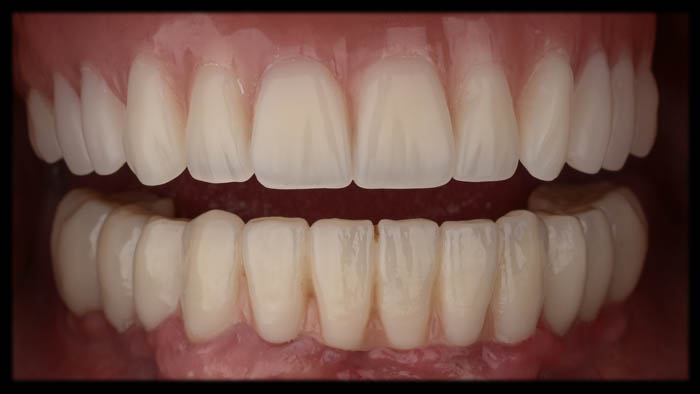
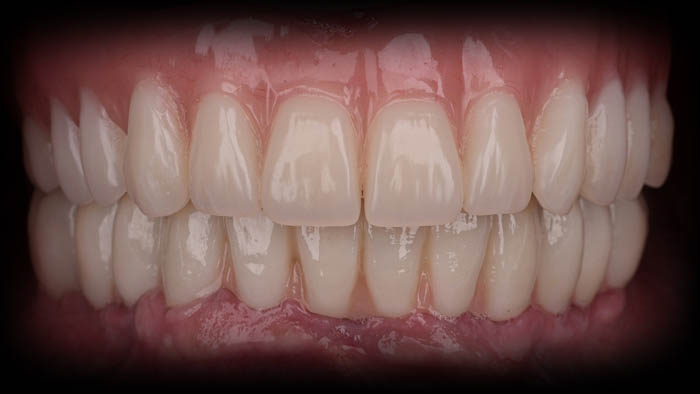
The patient was informed of the situation and opted to undergo reevaluation after one year, as well as being monitored during the next radiographic examination.
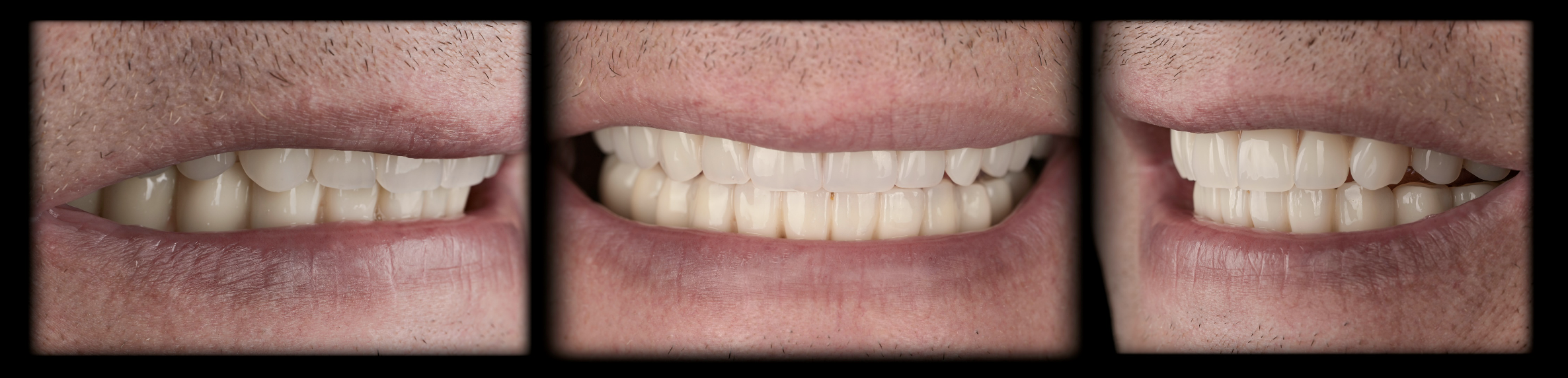
Thanks to the incredible progress of modern dentistry, we are now able to carry out treatment plans in much shorter time frames. But it's important to note that these advanced treatments require the expertise of a team of professionals, in order to meet the high standards of modern patients.


This case was done by Dr. Sławomir Pastor at Stomatologia Pastor in Legnica, Poland.